Understanding the complexity of changes and degeneration associated with KAND and other diseases affecting the brain is essential in helping our research community target appropriate treatment options. By studying human brain tissue, researchers can make discoveries for KAND as well as other diseases. Brain tissue research is an advanced, significantly impactful research option available to scientists through the gift of brain donation.
Through a partnership between KIF1A.ORG and Autism BrainNet, a compassionate process has been established for KAND families who would like to advance research through the gift of a brain donation, should their loved one pass away. Though this is a deeply saddening topic to approach with our KAND community, it is important to note that this does not indicate your loved one(s) could pass away from an early death caused by KAND or any other condition. It is best to approach these decisions in advance, regardless of the severity of KAND, instead of during the worst moment in time. This allows your family to be prepared to make this decision if such an unexpected or tragic situation were to occur. This partnership allows families to fulfill their wishes with compassionate support.
“Talking with family members about brain donation is a key aspect of long-term planning. These discussions are much less stressful when they occur in advance and minimize the burden of decision-making at the time of death. Long-term planning will also help ensure that a donor’s decision is respected.” —Autism BrainNet
What is Autism BrainNet?

Autism BrainNet is a collaborative network of scientific institutions consisting of three sites in the United States, and two international partnerships in Canada and the United Kingdom. Autism BrainNet collects, processes, stores, and distributes donated brain tissue to qualified researchers worldwide. Their mission is to work with researchers like our leading KAND researcher, Dr. Wendy Chung, and the communities affected by autism and other neurodevelopmental conditions to develop a sensitive and effective strategy for acquiring postmortem brain tissue. The donations will produce a resource that facilitates the highest quality research.
Why donate?
There is still so much to learn about how the brain works for those diagnosed with autism or a related neurodevelopmental condition like KAND. Allowing scientists to examine brain tissue facilitates a better understanding of changes in brain tissue and provides the opportunity for researchers to better identify treatments to improve quality of life for so many others living with these conditions. A brain donation is a meaningful way for donor families to contribute to science after the loss of a loved one. Donor families offer hope to others urgently seeking treatment.

“The gift that our families have given to the community has been just incredibly hard but so incredibly generous and so incredibly important for all of the kids and folks out there with KAND…With generous donations of the families, we’ve been able to start understanding what parts of the body are affected, what parts of the nervous system are affected, and we have some sense now of which parts are most sensitive. In terms of being able to think about where we need to give a drug or where we need to give a therapy…It’s a very practical question that we would not have been able to know without being able to see the brain. With each child’s brain, we’ve learned more and more. For those of you who are parents or family members of those angels, I can’t tell you how much your contribution has meant to the entire community and for generations until we cure this.”
—Dr. Wendy Chung, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, speaking at the 2021 KAND Family and Scientific Engagement Conference
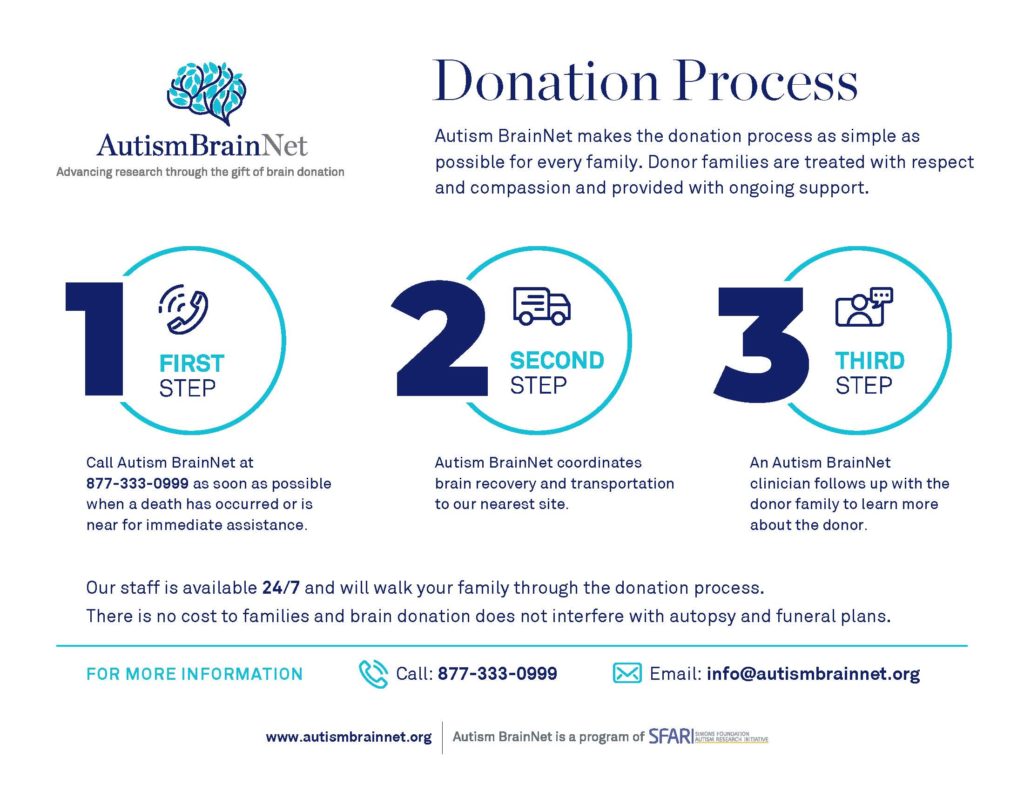
What is the donation process?
We highly recommend that your family visit Autism BrainNet’s website and read through their frequently asked questions for more detailed information. Here is a brief overview of the donation process:
There is no pre-registration or registry to give the gift of a brain donation. Consent from next of kin is required. Any pre-planning documents or healthcare directives can include the intent to donate brain tissue, if preferred.
Autism BrainNet partners with several family organizations, including KIF1A.ORG, to facilitate donations.
At the time of death or when death is near for a KAND patient, the next of kin or legal representative in the U.S. can call the Autism BrainNet 24/7 hotline at 877-333-0999 for immediate assistance, and mention the family is interested in a brain donation to Autism BrainNet for KAND research with Dr. Wendy Chung. Autism BrainNet will do everything they can to make the process as smooth as possible for families. Please also contact Kathryn Atchley, KIF1A mom and President of KIF1A.ORG, at 417-848-4881 for additional support.
At the time of death or when death is near for a KAND patient, the next of kin or legal representative can call the Douglas-Bell Canada Brain Bank at 514-761-6131 ext. 3496 or toll-free at 1-866-930-0291 and mention the family is interested in a brain donation to Autism BrainNet for KAND research with Dr. Wendy Chung. Every attempt will be made to make the process as smooth as possible for families. Please also contact Kathryn Atchley, KIF1A mom and President of KIF1A.ORG, by Facebook message, email (kathryn@kif1a.org) or phone at 1-417-848-4881 for additional support.
Families outside of the U.S. and Canada can reach Kathryn Atchley, KIF1A mom and President of KIF1A.ORG, by Facebook message, email (kathryn@kif1a.org) or phone at 1-417-848-4881 in an emergency. KIF1A.ORG and Chung Lab will work together to find a local organization that facilitates brain donation. We will do everything we can to make the process as smooth as possible for families.
Resources:
If you have any questions related to the donation process, you can contact Autism BrainNet at info@autismbrainnet.org. For additional support, please reach out to the KIF1A.ORG team at impact@KIF1A.ORG.
Some content on this page has been borrowed from Autism BrainNet.
Austim BrainNet. 2021, https://www.autismbrainnet.org/.